Feedback
Your work only gets better
Feedback is an integral part of the design process and should be sought out when designing anything, be it product, service, or system. In design, feedback is a multi-step phase during which the design gradually reaches farther and farther outward from the core team in order to gather feedback from an increasingly large pool of feedback providers.
Skip ahead
Feedback & revision process map Strategies for feedback What to do with feedback: make changes Bringing it all together A note on using feedbackIt’s preferable to gather feedback on several of the team’s design iterations. Through feedback, the team is able to understand which design ideas might hold up best in real-world conditions and which ones resonate most with participants. Feedback also allows the team to improve and refine the design iterations, using the feedback reviews to gradually phase out the design iterations that are less successful while refining and focusing the more successful ones.
In this section, see the cycle of feedback and revision for a single design solution. Two steps make up a feedback phase: (1) receiving the feedback from an individual or group and (2) making revisions to the product, service, or system based on that feedback. In each feedback step, the circle of people the team reaches out to for feedback moves farther away from the core team and farther into the field of potential participants.
These feedback sessions can take the form of codesign workshops, prototype testing, or other formats depending on the product, service, or system being tested. Guidance on different feedback formats will appear in the Design Phase Operations Guide. For the second step, design revision, the team revises the design internally in order to integrate the feedback from the people that have been asked. Revision activities generally take the shape of tiny synthesis sessions; you will find guidance on those in the Operation Guide as well.
Feedback & revision process map
This Feedback and Revision Process is a basic framework for how to seek out and integrate feedback into a product or service you have designed. Before jumping into the feedback loops, the team needs to review the primary Design Phase principles as well as the principles you developed during Problem Framing. After an intense iteration phase, in which the team gets deeply involved in details, a refocus onto the participants and the strategic level goals of the project will prove useful.
There are two parts to the feedback process:


Strategies for feedback
Creating a strategy for feedback allows the team to collect feedback logically and methodically. The team should test with people who are all current participants or future participants in the product, service, or system that is being created, but those participants can and should be from different areas of the design object’s use. For example, if you test with a front-line participant at one stage of testing, you should try to balance that by testing with a leadership level participant at another. Of course, it’s not always possible to perfectly construct feedback testing rounds; the purpose of this guidance is not to create an impossible goal of perfection for testing, but to give guiderails on the best way the team can go about this process.
If testing narrows in on a single participant group for reasons of access or timeline, that’s okay, but it will result in a not-as-thoroughly testing tested prototype. For this reason, the designed product, service, or system’s potential for success is lessened. While this is sometimes acceptable, it is not desirable. Work with your leadership to find a way to either extend your team’s timeline or to gain access to the participants you need.
Who to talk to: an expanding galaxy
In testing rounds, the design team needs to get feedback from people who have increasing amounts of distance from the project. This is for two reasons:
- Starting with participants previously involved in or aware of the project allows the team to test low fidelity prototypes with people who have context on the project itself. This will provide actionable feedback to increase the refinement of that prototype quickly.
- Moving outward to people who have no relationship to or awareness of the project includes the perspective of absolutely new participants. This allows the design team to learn about and correct for the issues new users will have without having to find out those issues during a pilot.
This group will also encounter a closer-to-launch-fidelity prototype, which prepares them for interacting with the new product, service, or system during the pilot phase.

Round 1
An ideal person for round 1 feedback is someone who has previously been involved in the project and is familiar with
the research or design of phases of it. This can be one of your primarily research or design partners.
Round 2
A good type of person for round 2 feedback is someone who is close to but not directly involved in the research or
design of it. This can be the teammate of one of the Round 1 feedback people who you simply haven't talked to
directly before.
Round 3
It’ useful for round 3 feedback to talk to someone who is aware of the project, but not previously involved in
the research or design. This can be another teammate of people in Rounds 1 or 2 but, for whatever reasons, has been
somewhat distanced from the project development.
Round 4
A strong candidate for round 4 feedback is a person who has not previously been in touch with the team or the other
participants about this project at all. This person’ fresh eyes will help head off any quirks or stumbling
blocks that, due to familiarity, the previous testers might have taken for granted.
What to do with feedback: make changes
Each time the team gathers feedback on the designed product, service, or system, document, meet, and discuss that feedback. Think of this process as a smaller, more concentrated version of the Problem Framing process the team underwent during the early parts of your Discovery Phase. In that process, as new information about the large problem frame was uncovered through desk research and the identification of constraints, the team narrowed in on the specific problem frame in which you were going to operate. Similarly, in this process, as the team tests with participants, you will make changes to your prototype to narrow in on a more useful and resonant product, service, or system for your participants.
You’ work with the resources you have, within the constraints of the product, service, or system you first designed based on your research, to better fit the needs of the ultimate participants in your work. This means tweaks, not systematic changes.

If, at this point, you find the need for large scale, thematic or systematic changes, it means the design that you’ forwarded does not accurately reflect the opportunities identified in the Discovery phase, so the team will need to start again on the design process. This outcome is not failure; indeed, it simply means you know more about what your participants need. And, if you’ designed in quick, fast iterations, you’ easily be able to go back and change your direction without adding a great deal of cost or time to your project.
Below, find another visualization of making small changes based on feedback. As you can see, the tangram shape stays roughly the same shape through all the revisions. They all, vaguely, look like a person standing up in different poses. Those different poses are created by moving around some of the pieces that make up the puzzle. These changes are analogous to the changes the design team should be making in the feedback cycle: ones that change details to the overall design, but not the core idea of the design itself.
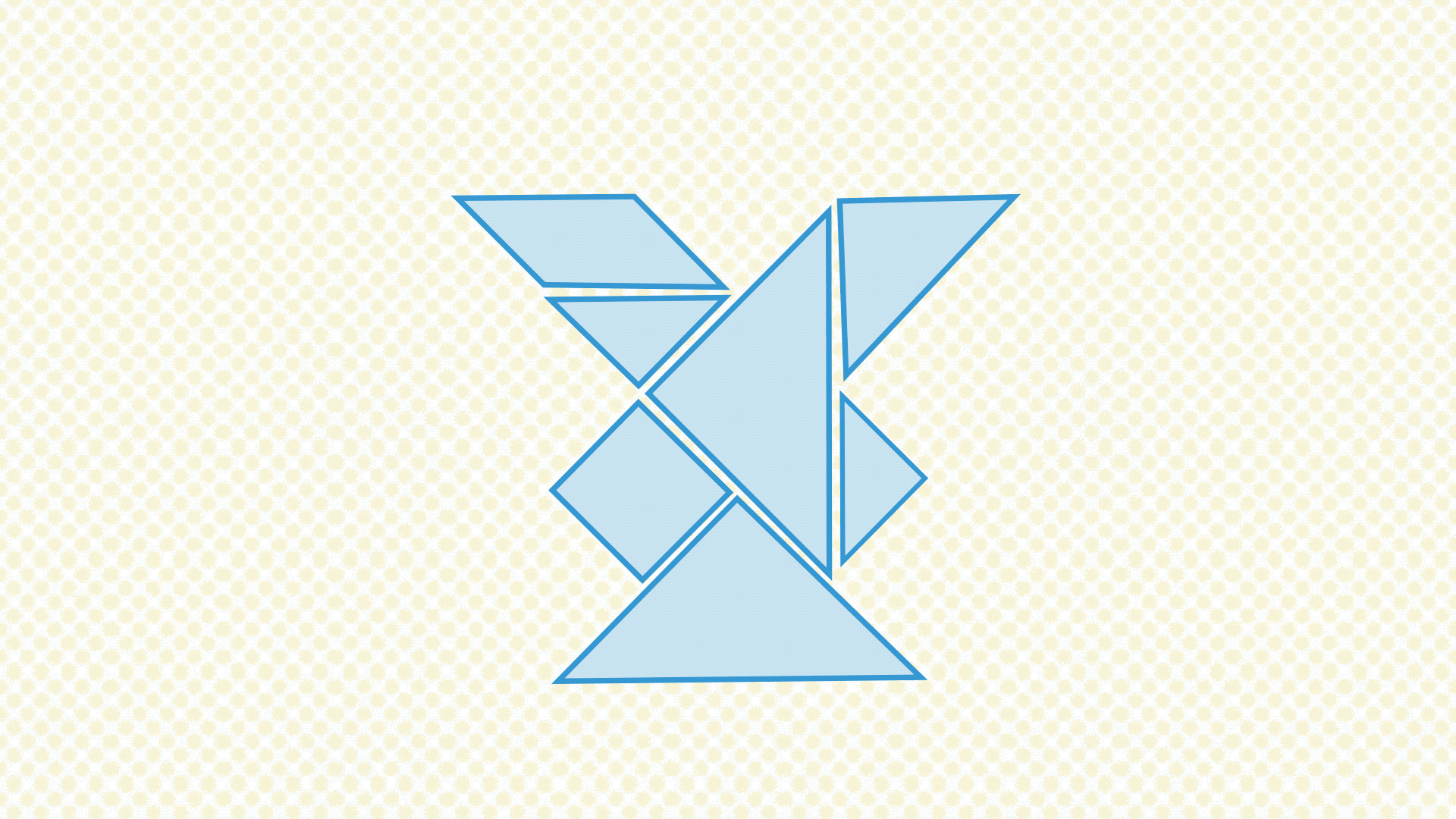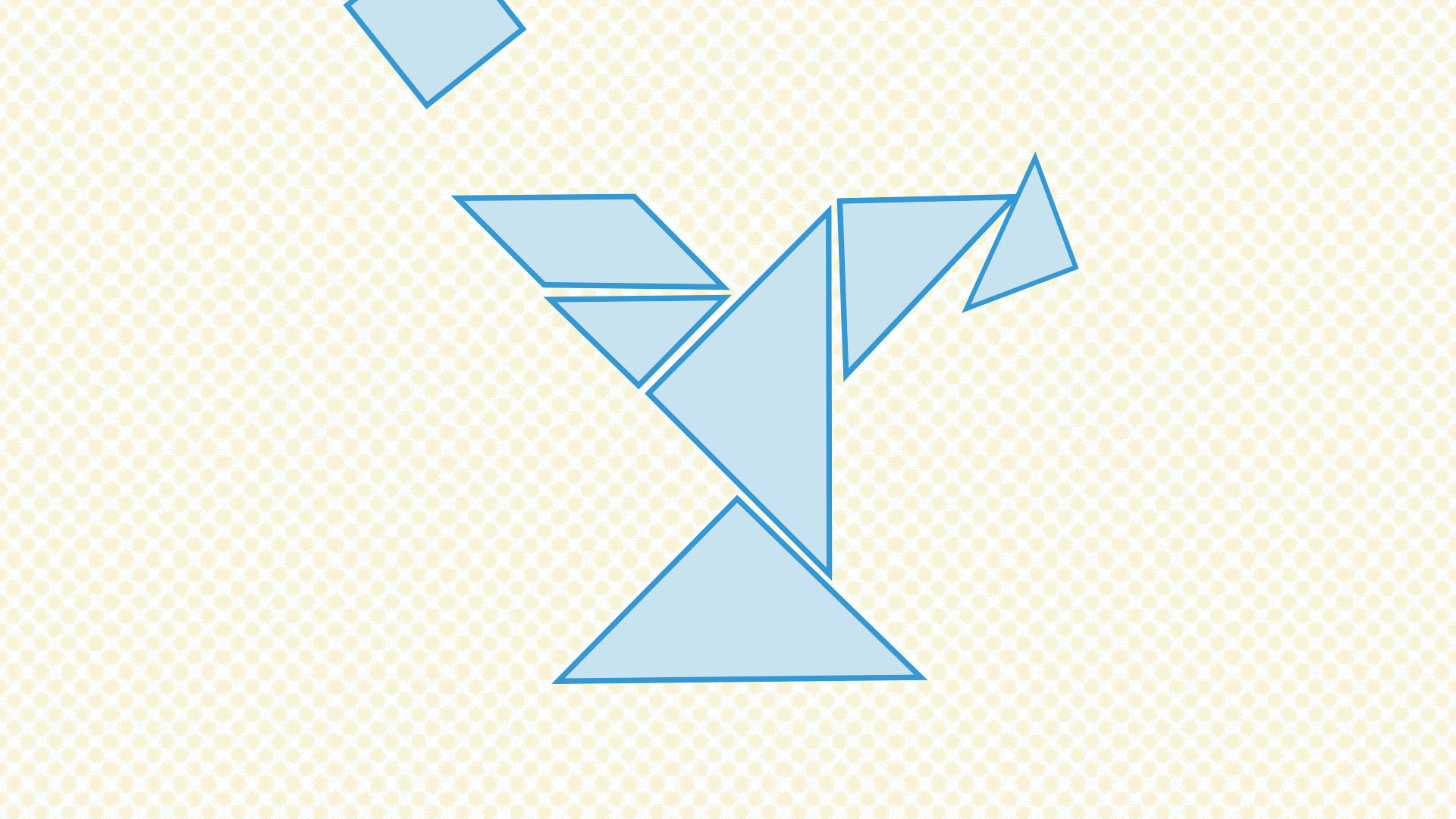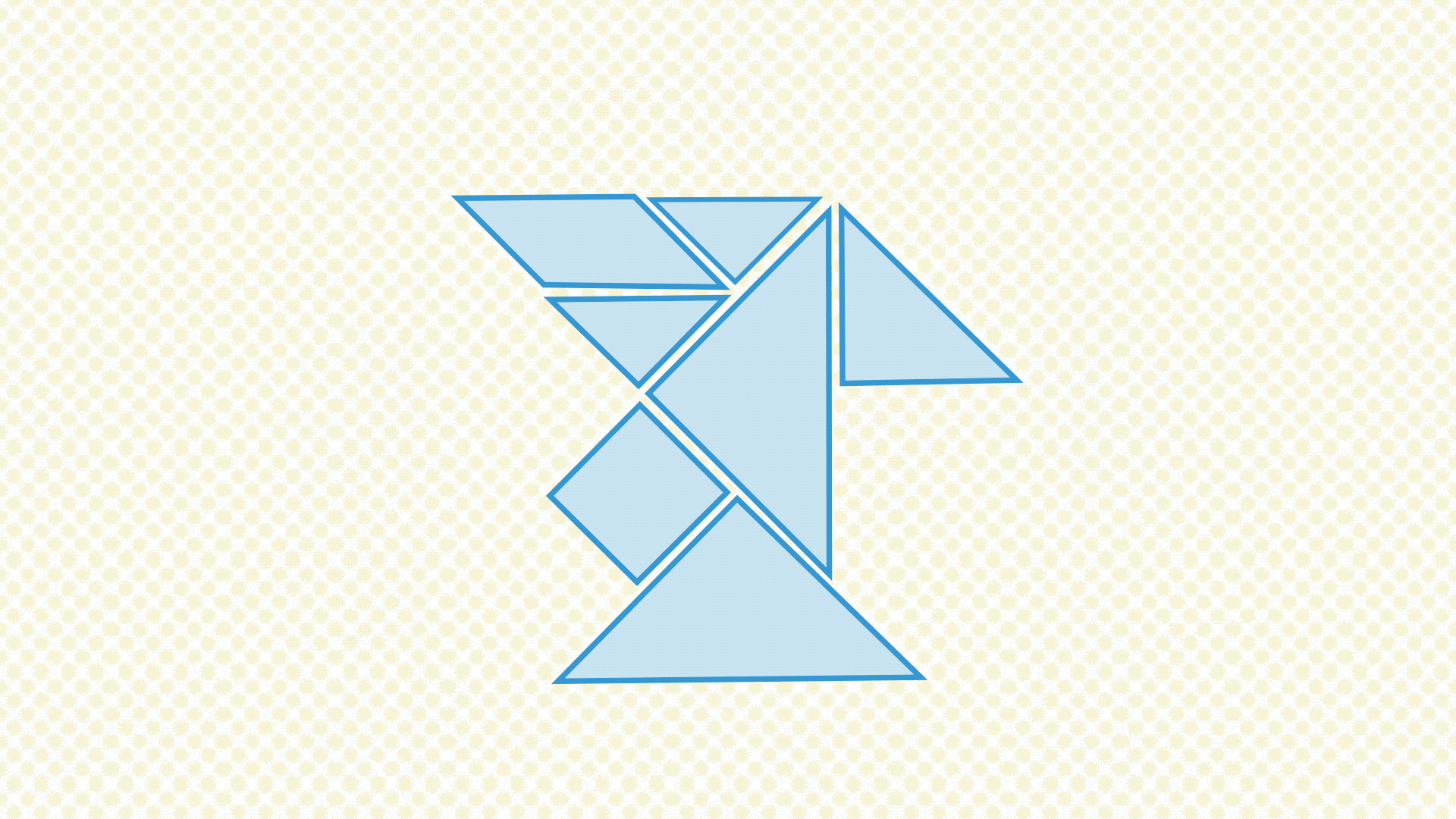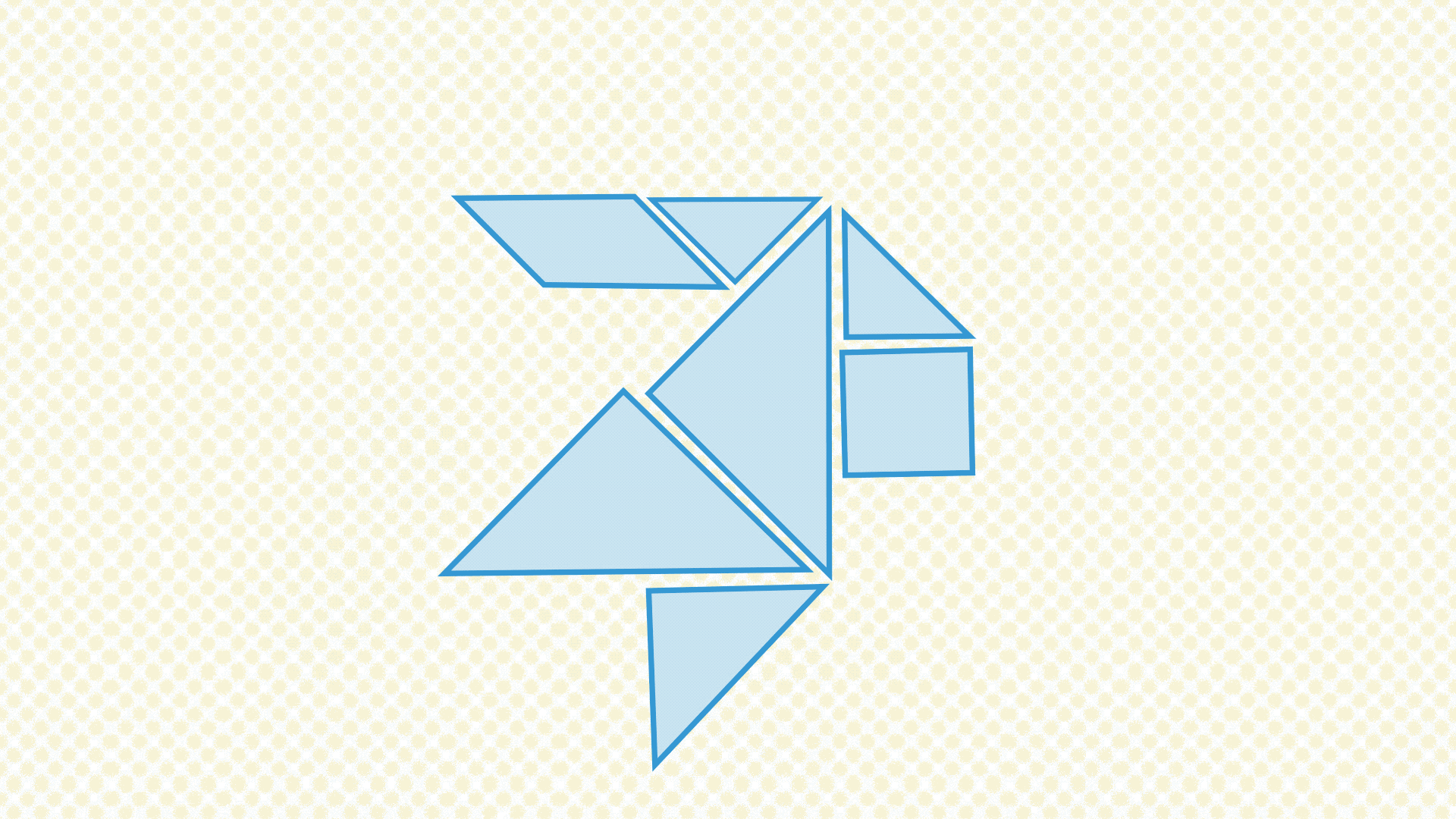
Bringing it all together
Through the feedback cycle, the team will talk to a variety of people to gather feedback on the product, service, or system the team is designing. Those people will have different positions to and awareness of the project and its history. As you gather feedback from these people, the team will make changes to its design in response to that input.
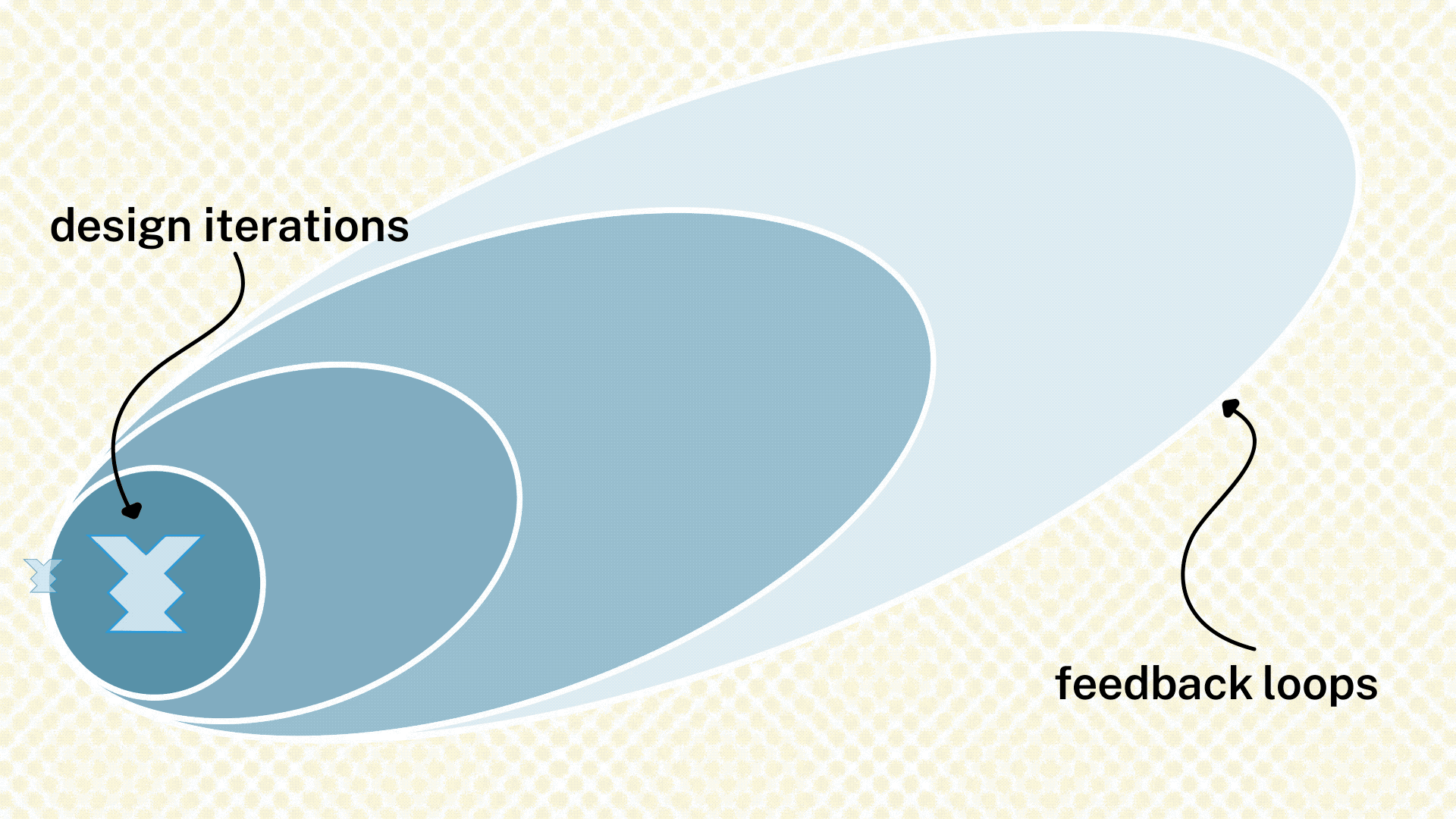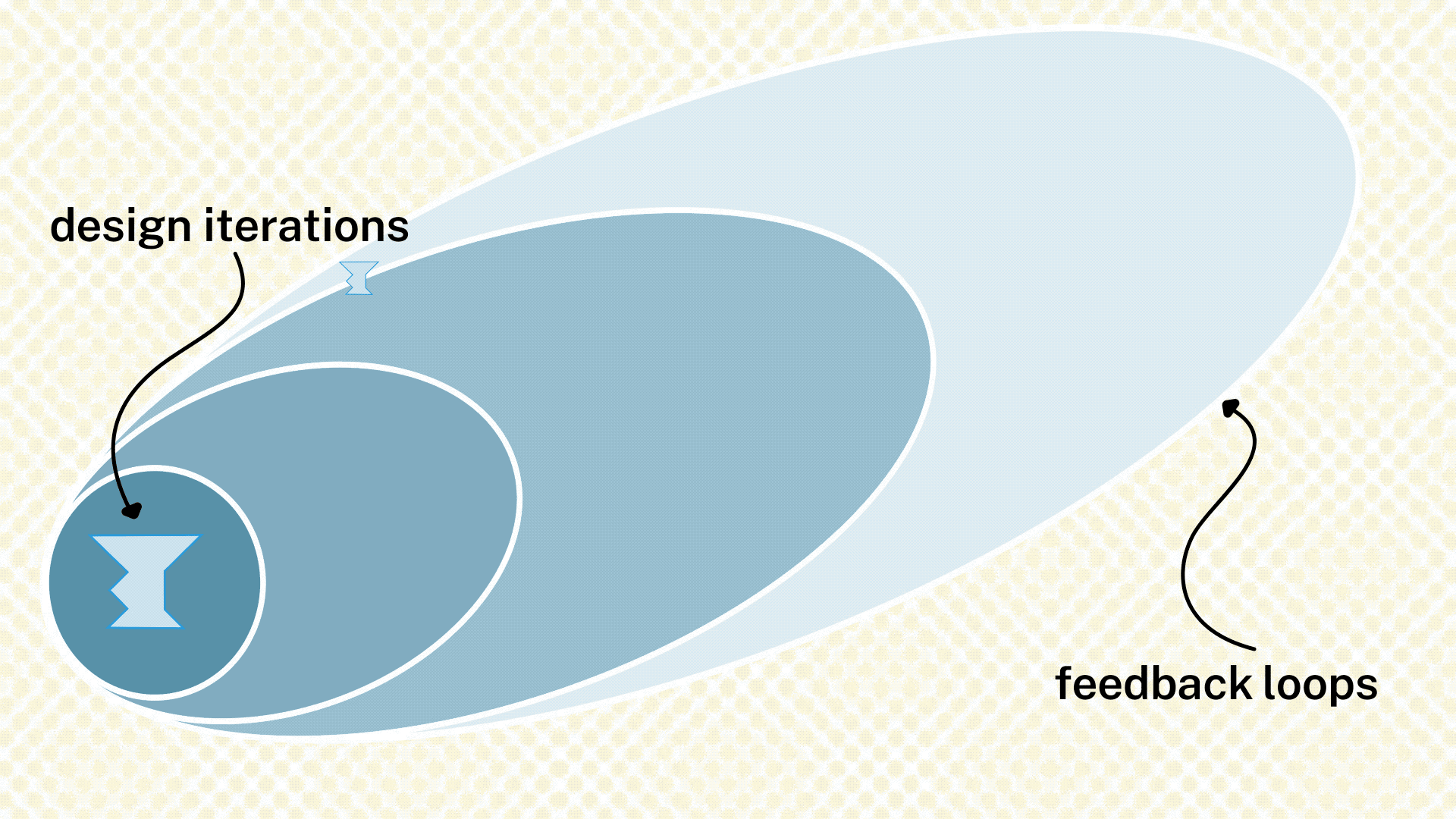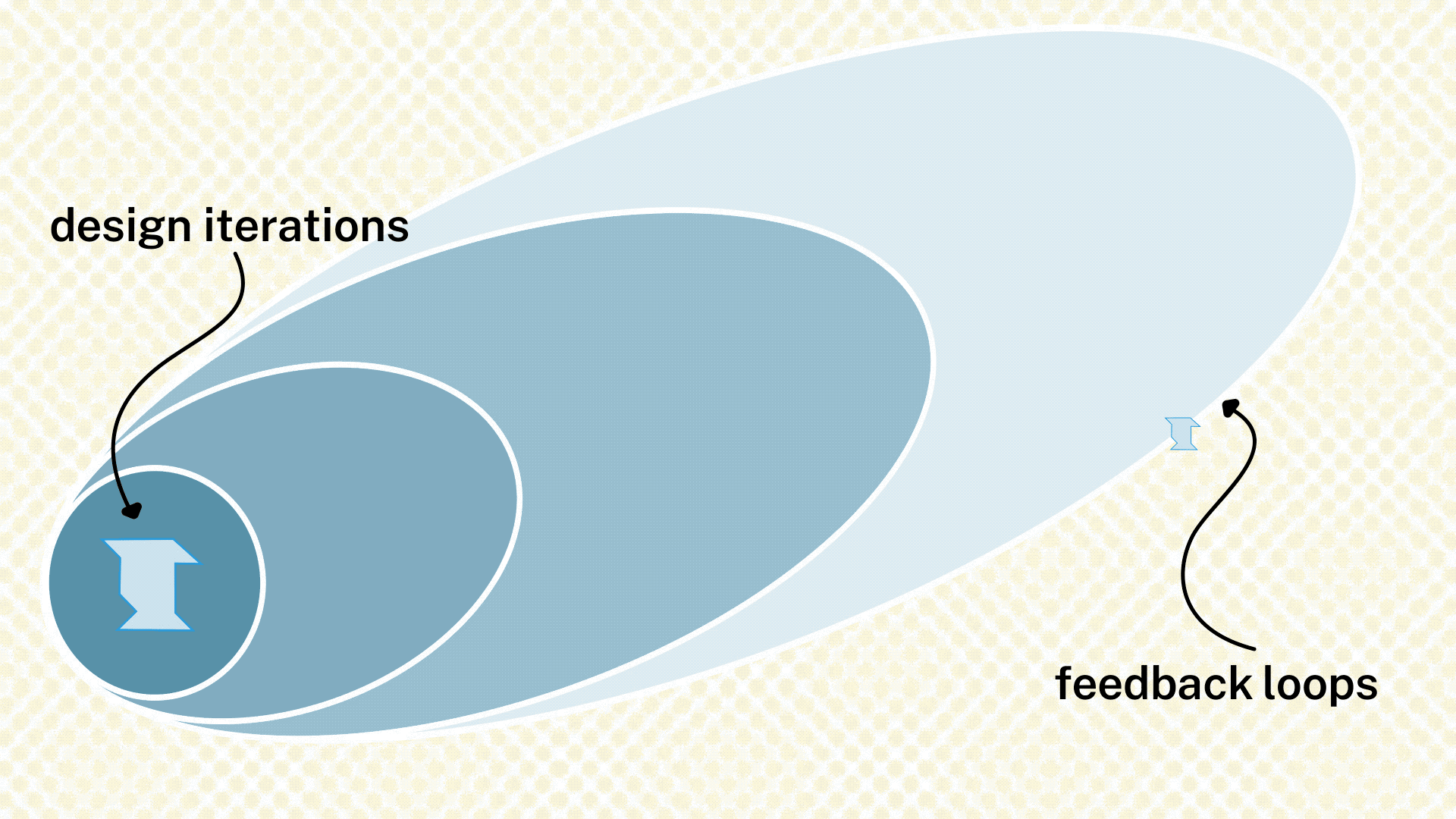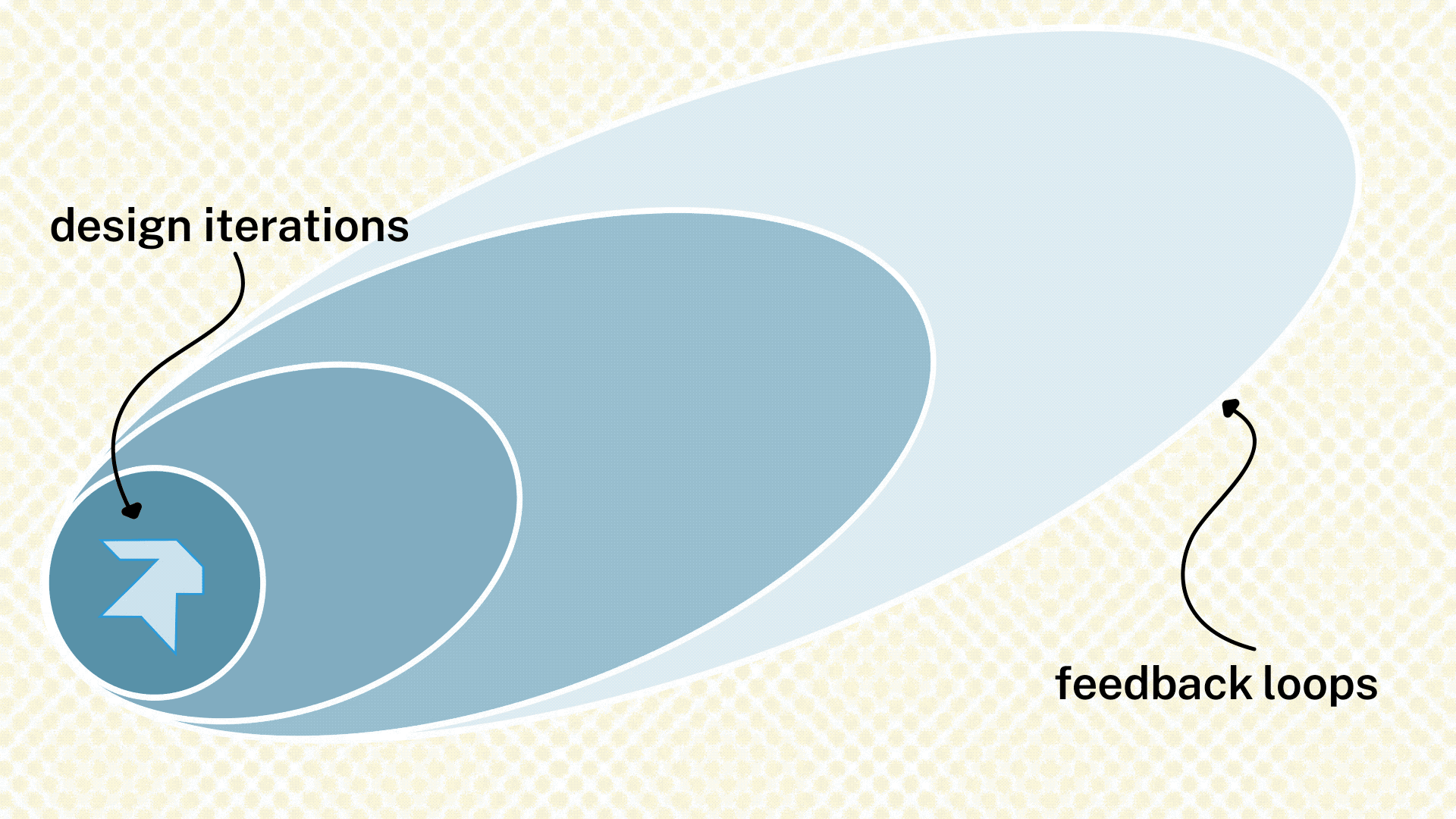
If the feedback points the team to an entirely different design, that’ okay, but the team must throw out its design and start the design process itself again. In this case, the team might want to review their Opportunities from their Discovery Phase and identify a new direction in which to go for their new design.
A note on using feedback
It is important to know that not every piece of feedback from each participant can should be integrated. Be aware of the primary principles of the design phase (and review them if you need to) as well as the principles from your problem framing phase.
If your design resonates deeply, people will be excited about its potential, have great ideas for improvements, and really want to see those improvements. Ensure that you compare those suggestions to your original project scope and technical ability. If you cannot integrate an improvement into this stage, that’s okay. Communicate to the participant that their feedback is well-placed and important, and that you will note it for integration into a future version or as an idea for a related product or service.